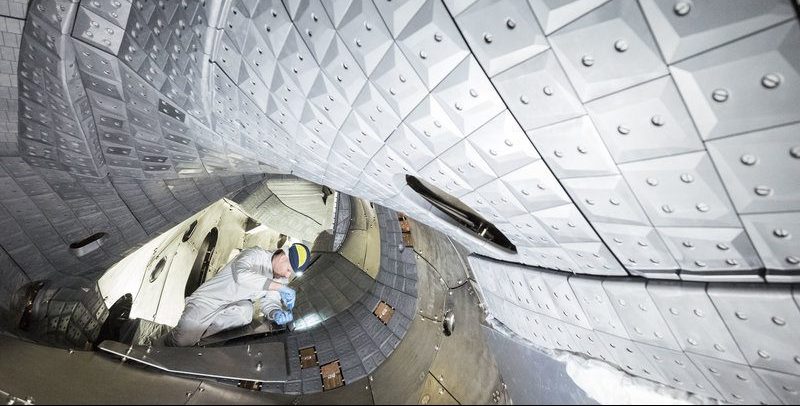
In the past experimentation round, Wendelstein 7-X achieved the stellarators’ world record for the fusion product as a result of reaching higher temperatures and densities of the plasma as well as longer pulses. Wendelstein 7-X attained a fusion product of 6·1026 degrees x second per cubic metre which is the world’s stellarator record and gives first confirmation that the optimisation carried out for its design has been successful.



 The Divertor Tokamak Test (DTT) Facility will be built in Frascati, Rome, Italy, as has been announced by
The Divertor Tokamak Test (DTT) Facility will be built in Frascati, Rome, Italy, as has been announced by